Pneumonia and aerosacculitis due to Aspergillus fumigatus in quails
We received different inquiries from an avian slaughterhouse in which lesions were observed in different quail batches during post mortem examination. The lesions occupied a great portion of the celomic cavity and had a nodular appearance. Whole carcasses were submitted to SESC to confirm its diagnosis.
Upon reception, the carcasses were subjected to complete necropsy, which revealed a big number of masses of approximately 1cm of diameter in the celomic cavity, that revealed a white dense caseous content and a big fibrous capsule when sectioned. The lesions were distributed in the air sacs, mostly centered around the pulmonary region, however, in the most severe cases they affected the whole air sacs occupying a great proportion of the celomic cavity (without involving the viscera). Samples from the different granulomas were collected and submitted to the microbiology laboratory, histology was also performed.
The granulomas, histologically, were composed of a big necrotic core surrounded by a rim of epithelioid macrophages and multinucleated giant cells, with a thick fibrous capsule and lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. In the interior of the granuloma, between the necrotic debris, multiple fungal hyphae were observed, displaying septation, parallel walls and dichotomic ramification, which were compatible with ascomycetes fungi. A Grocott stain was also performed, revealing abundant fungal structures.
The fungal culture resulted in the abundant growth of fungal colonies compatible with Aspergillus fumigatus, confirming it was the causal agent. In one of the cases, aside from the Aspergillus fumigatus bacteria were also isolated from the lesions (E. coli, Enterococcus sp.).
Avian aspergillosis is often found in its respiratory form, with multiple granulomas involving the lungs and air sacs. Also an alimentary form is described, affecting the crop, gizzard and proventriculum amongst others. Although its possible, the systemic dissemination of the aspergillosis is not a frequent event, hence it usually presents as either one of the two forms reflecting the route of infection. In broilers and laying hens, it usually reflects bad environmental conditions or a big degree of immune suppression of the animals. In quails it appears as a rather frequent condition, although it is not clear if the animals are naturally more susceptible to infection. (AC)
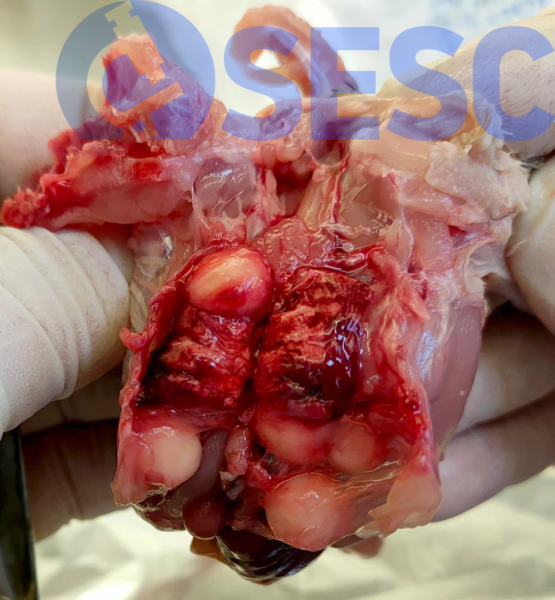
Half quail carcass. Once the costal wall and viscera were removed, multiple granulomas involving lungs and air sacs were observed.
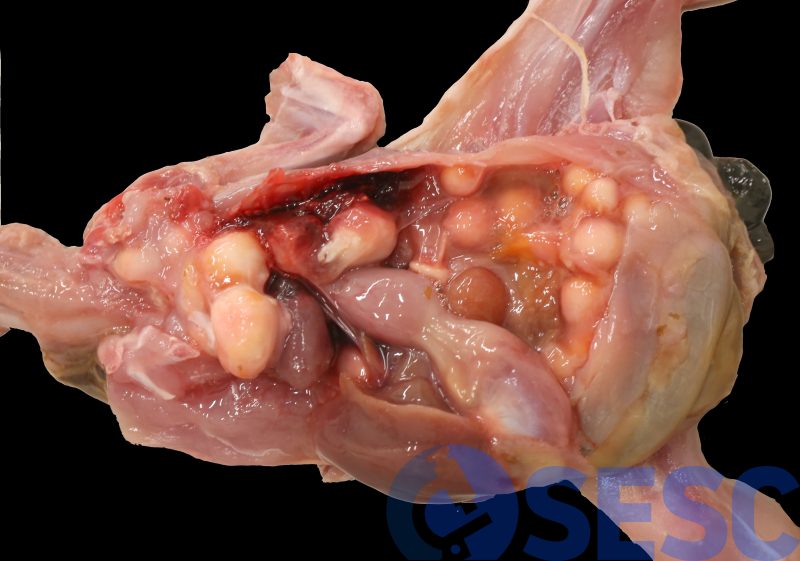
Quail carcass. Very abundant granulomas could be observed in the air sacs, occupying a big space in the celomic cavity.
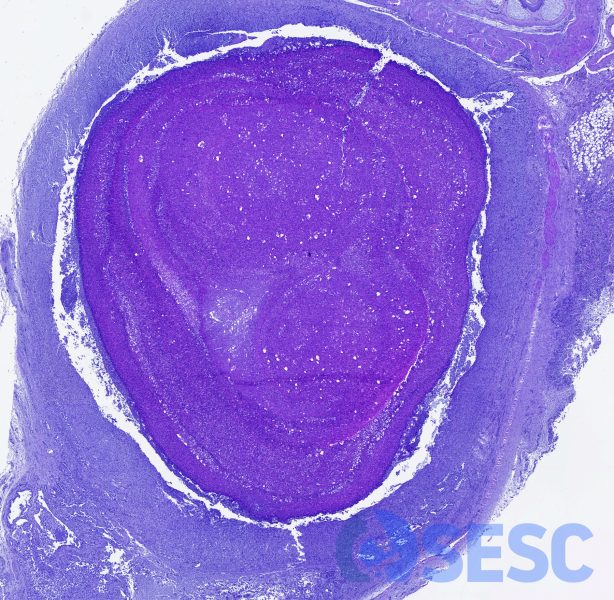
Histologic view at low magnification of one of the granulomas. A big necrotic core could be observed, surrounded by a rim of macrophages and mature fibrous tissue.
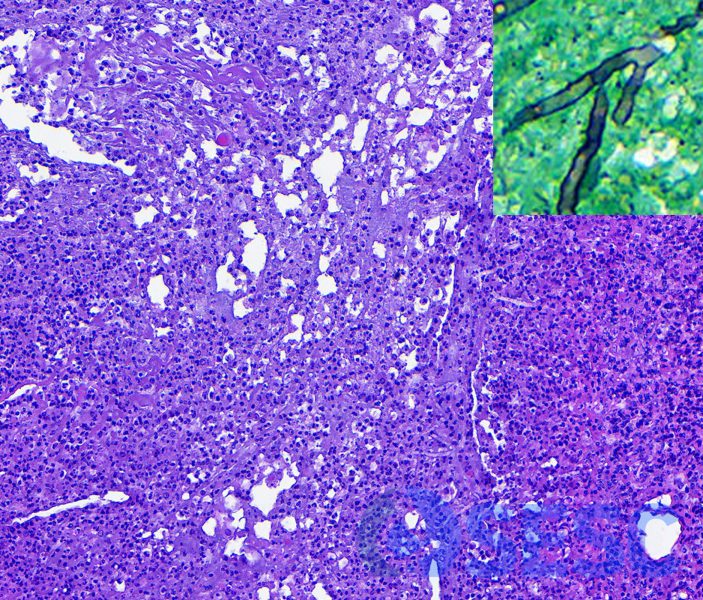
In the center of the granuloma at higher magnification, abundant cellular necrotic debris and degenerated heterophils were found along with multiple fungal hyphae. They were more evident at the Grocott stain (inset).
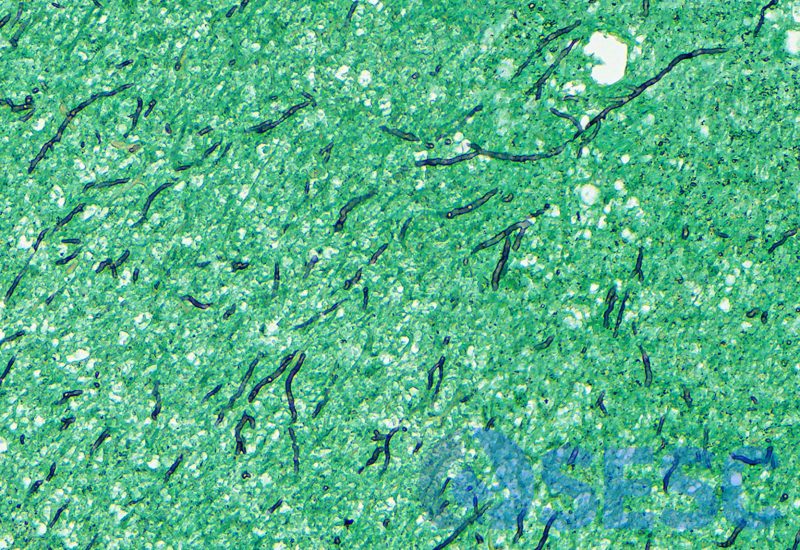
Groccot stain at lower magnification, in which abundant fungal hyphae could be observed, displaying parallel wall and dichotomic ramifications (compatible with ascomycetes).
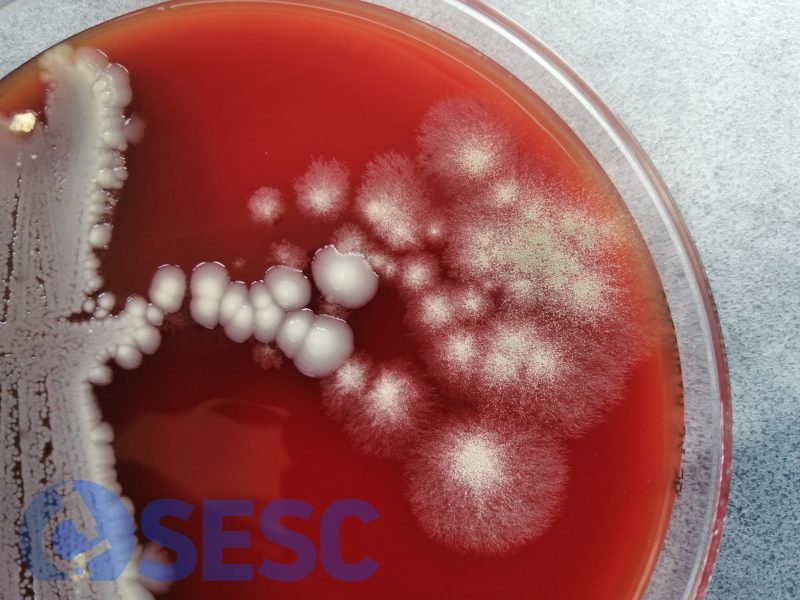
Fungal culture revealing abundant growth of fungae compatible with Aspergillus fumigatus.

