10/03/2014
|
Poultry
0
Múltiple lesions in an organic chicken carcass
Pathologic examination of the animal allowed to observe different types of lesion without any apparent link between them :
- The skin of the back had a multifocal ulcerative bacterial dermatitis, heterophilic and crusty, moderate and chronic with abundant intralesional bacteria.
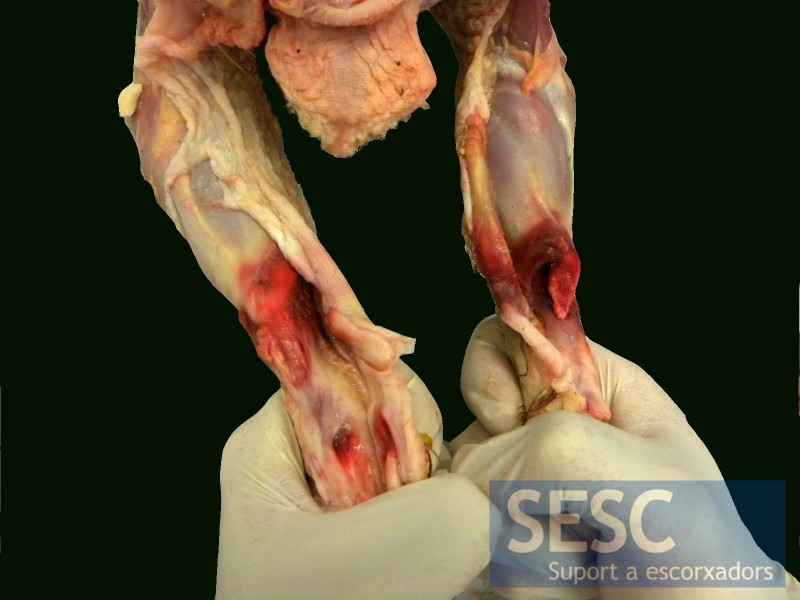
- The examination of the lesions in the tarsus revealed a viral arthritis with bilateral rupture of the gastrocnemius tendon and severe chronic tenosynovitis. This lesion is characteristic of avian reovirus infection.
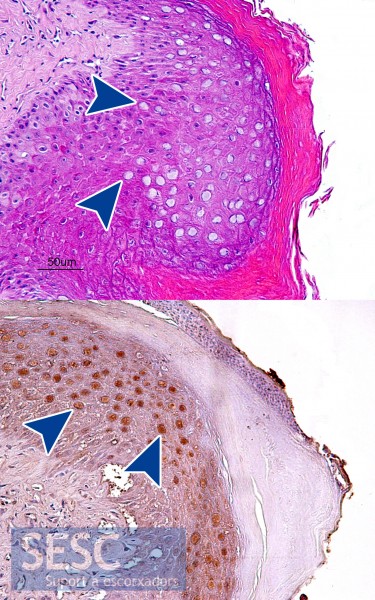
- Lesions on the comb corresponded to a hyperplastic and ulcerative severe, multifocal to diffuse dermatitis with intranuclear inclusion bodies. This type of lesion is indicative of a viral etiology. Although the inclusion bodies were positive to immunohistochemistry for papillomavirus, its presence could not be confirmed by electron microscopy.
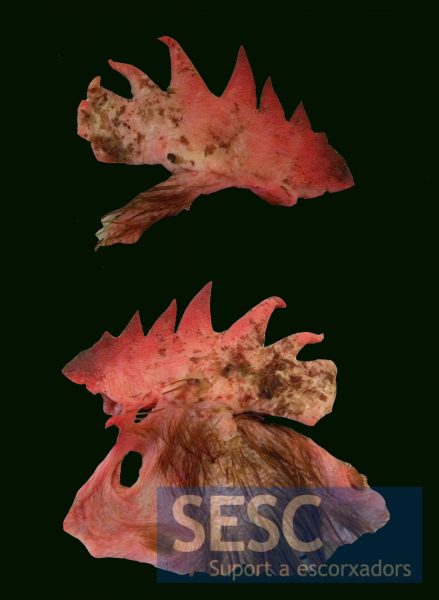
The comb had confluent multifocal areas of hyperplasia, ulceration and crust, of between 0.5 to 1 cm in diameter.